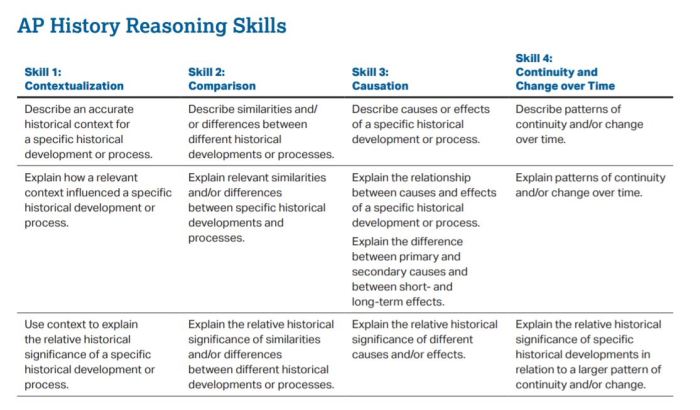
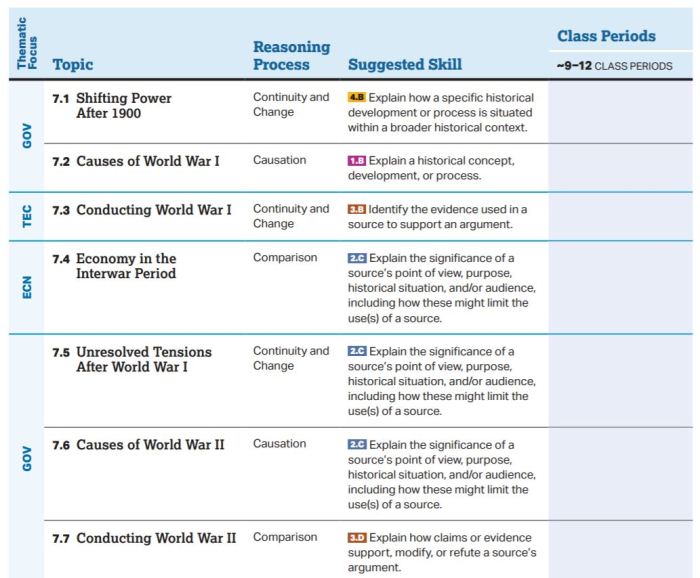
Embark on an intellectual journey with our comprehensive guide to AP World Unit 7 LEQ prompts. Dive into the complexities of World War II, examining the diverse historical perspectives, diplomatic blunders, and their profound impact on the course of human history.
From the outbreak of hostilities to the war’s far-reaching consequences, this exploration unravels the intricate tapestry of events that shaped the 20th century and continues to resonate in contemporary international relations.
Analyze Historical Perspectives

Various historical perspectives have shaped our understanding of the causes of World War II. Each perspective offers a unique lens through which to examine the complex factors that led to the outbreak of the war.
Traditionalist Perspective
This perspective emphasizes the role of traditional diplomatic factors, such as secret treaties, alliances, and territorial disputes. Traditionalists argue that the war was primarily caused by the failure of diplomacy and the breakdown of the European balance of power.
Revisionist Perspective
Revisionists challenge the traditionalist view, arguing that economic and ideological factors played a more significant role in the war’s outbreak. They contend that the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh reparations on Germany after World War I, created economic instability and resentment that contributed to the rise of fascism and militarism.
Marxist Perspective
Marxists view the war as a product of capitalism’s inherent contradictions. They argue that the war was a struggle between rival capitalist powers for control of resources and markets.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Each perspective offers valuable insights into the causes of World War II, but they also have their limitations.
- Traditionalist Perspective:Strength: Emphasizes the importance of diplomatic failures. Weakness: May overlook other contributing factors.
- Revisionist Perspective:Strength: Highlights the role of economic and ideological factors. Weakness: Can underestimate the impact of diplomatic tensions.
- Marxist Perspective:Strength: Provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the war’s origins. Weakness: May oversimplify the complex interplay of factors.
Examine Diplomatic Failures

The outbreak of World War II was not inevitable. A series of diplomatic failures played a key role in escalating tensions and ultimately leading to the conflict.
One major failure was the failure of the League of Nations to prevent aggression. The League was created after World War I to promote peace and prevent future conflicts. However, it proved to be ineffective in stopping the rise of aggressive regimes such as Nazi Germany and Japan.
Failure of Appeasement
Another diplomatic failure was the policy of appeasement pursued by Great Britain and France in the 1930s. Appeasement was an attempt to avoid war by giving in to the demands of aggressive powers. However, it only served to embolden Hitler and other dictators.
Lack of Communication
Finally, there was a lack of communication between the major powers. The United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union all had different interests and goals. They were unable to find common ground and work together to prevent the outbreak of war.
The diplomatic failures that led to World War II were complex and multifaceted. They involved a combination of factors, including the failure of the League of Nations, the policy of appeasement, and the lack of communication between the major powers.
Assess Military Strategies

The military strategies employed by the Axis and Allied powers during World War II were diverse, reflecting the unique strengths and weaknesses of each side. This essay will compare and contrast these strategies, analyzing their effectiveness in different theaters of war and discussing the impact of technology and innovation on military operations.
Axis Strategies
The Axis powers, led by Germany, Japan, and Italy, pursued a strategy of aggression and territorial expansion. They sought to gain control of key resources and strategic positions, using blitzkrieg tactics to overwhelm their opponents with rapid, concentrated attacks. In Europe, Germany’s Wehrmacht utilized the “lightning war” approach, relying on mobility, air power, and armored units to penetrate enemy lines and encircle their forces.
In the Pacific, Japan employed a similar strategy, using its naval superiority to launch surprise attacks and seize islands in Southeast Asia. They also employed kamikaze pilots, sacrificing themselves in suicide attacks against Allied ships.
Allied Strategies
The Allied powers, led by the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union, adopted a more defensive and reactive strategy. They aimed to contain Axis aggression and eventually liberate occupied territories. The Allies utilized a combination of conventional warfare, industrial production, and strategic bombing campaigns to wear down their opponents.
In Europe, the Allies initially focused on defending against German advances, using trench warfare and defensive tactics. As the war progressed, they gradually gained the upper hand, thanks to their superior resources and technological advancements.
In the Pacific, the Allies relied on their naval power to isolate Japan and cut off its supply lines. They also employed “island hopping” tactics, capturing strategic islands to establish air bases and bring Japan within range of bombers.
Impact of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation played a crucial role in shaping the military strategies of both sides. The development of new weapons, such as radar, jet aircraft, and atomic bombs, had a profound impact on warfare. Radar allowed the Allies to detect enemy aircraft and ships, while jet aircraft gave them an advantage in air combat.
The atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 marked a turning point in the war, demonstrating the devastating power of nuclear weapons. This ultimately led to Japan’s surrender and the end of the war.
Evaluate Social and Economic Impacts
World War II had a profound impact on societies and economies worldwide. It led to significant social upheaval, economic devastation, and a reshaping of global power dynamics. The long-term consequences of the war continue to shape the world we live in today.
AP World Unit 7 LEQ prompts can be challenging, but they also provide an opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of the material. One way to prepare for these prompts is to read widely on the topic. For example, you might read an article like Show Rite Fat and Fluffy to learn about the impact of the Industrial Revolution on the environment.
By reading widely, you can develop a deeper understanding of the key concepts and themes that are likely to appear on the LEQ prompts.
Social Impacts
The war had a devastating impact on populations around the world. Millions of people were killed, injured, or displaced. The war also led to widespread social upheaval, as families were torn apart, communities were destroyed, and social norms were disrupted.
- Loss of life:The war resulted in an estimated 40-85 million deaths, including military personnel and civilians.
- Displacement of populations:Millions of people were forced to flee their homes due to the war, creating a massive refugee crisis.
- Disruption of families and communities:The war separated families, destroyed homes, and uprooted communities.
- Social unrest:The war led to widespread social unrest, as people struggled to cope with the loss, displacement, and disruption caused by the conflict.
Economic Impacts, Ap world unit 7 leq prompts
The war also had a devastating impact on the global economy. The destruction of infrastructure, the loss of human capital, and the disruption of trade led to a sharp decline in economic output. The war also led to a massive increase in government debt, as countries borrowed heavily to finance their war efforts.
- Destruction of infrastructure:The war caused widespread destruction of infrastructure, including factories, bridges, and transportation systems.
- Loss of human capital:The war led to the deaths and injuries of millions of people, including many skilled workers and professionals.
- Disruption of trade:The war disrupted global trade, as countries imposed blockades and restrictions on the movement of goods.
- Government debt:The war led to a massive increase in government debt, as countries borrowed heavily to finance their war efforts.
Propaganda and Censorship
During the war, governments used propaganda and censorship to shape public opinion and control information. Propaganda was used to promote support for the war effort and to demonize the enemy. Censorship was used to suppress dissent and to prevent the spread of information that could damage morale or undermine the war effort.
- Propaganda:Governments used propaganda to promote support for the war effort and to demonize the enemy.
- Censorship:Governments used censorship to suppress dissent and to prevent the spread of information that could damage morale or undermine the war effort.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of World War II are still felt today. The war led to the division of Europe into two blocs, the East and the West, and to the Cold War. The war also led to the creation of the United Nations, which was established to prevent future conflicts.
The war also had a profound impact on the global economy, as it led to the rise of the United States as a superpower and to the decline of European colonialism.
- Division of Europe:The war led to the division of Europe into two blocs, the East and the West, and to the Cold War.
- Creation of the United Nations:The war led to the creation of the United Nations, which was established to prevent future conflicts.
- Rise of the United States:The war led to the rise of the United States as a superpower.
- Decline of European colonialism:The war led to the decline of European colonialism.
Discuss Historiography and Legacy
The historiography of World War II has evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing perspectives and the availability of new sources. Initially, the war was seen as a straightforward conflict between good and evil, with the Allies representing the forces of democracy and freedom against the Axis powers of fascism and tyranny.
However, as more information became available, historians began to question this simplistic narrative.
Ongoing Debates and Controversies
One of the most controversial aspects of World War II is the decision by the United States to drop atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Some historians argue that the bombings were necessary to end the war and save lives, while others believe that they were an unnecessary act of mass murder.
Another ongoing debate is the role of the Soviet Union in the war. Some historians argue that the Soviet Union played a crucial role in defeating Nazi Germany, while others believe that its contributions have been exaggerated.
Expert Answers: Ap World Unit 7 Leq Prompts
What are the key diplomatic failures that led to World War II?
The failure of the League of Nations, the appeasement policy towards Nazi Germany, and the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact were among the critical diplomatic failures that contributed to the outbreak of World War II.
How did the military strategies of the Axis and Allied powers differ?
The Axis powers employed a strategy of Blitzkrieg, emphasizing rapid and overwhelming attacks, while the Allied powers adopted a more defensive approach, relying on industrial production and strategic bombing.
What were the long-term consequences of World War II on global society?
The war had profound social and economic impacts, including the displacement of millions of people, the rise of superpowers, and the establishment of the United Nations.