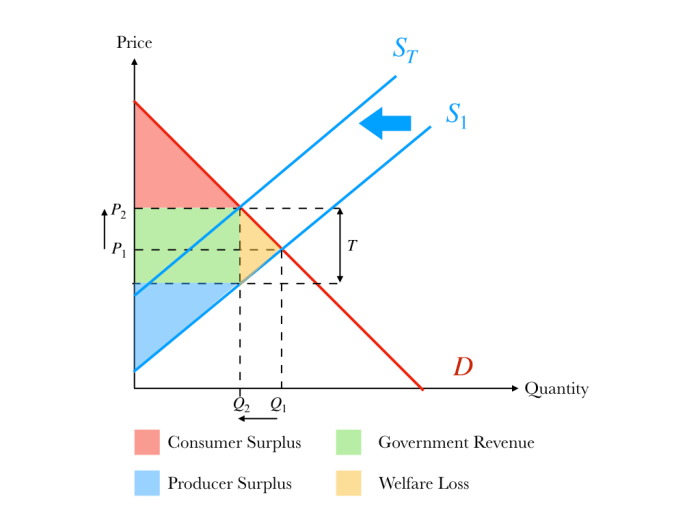
With micro topic 2.8 effects of government intervention at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights. Government intervention, a topic that has sparked countless debates and shaped economic landscapes, takes center stage as we delve into its profound effects on economic growth, income distribution, market efficiency, and specific industries.
Prepare to unravel the complexities of government’s role in shaping economic outcomes, as we explore both the positive and negative consequences of its interventions.
This comprehensive analysis will provide a clear understanding of the various types of government interventions, their intended goals, and the factors that influence their effectiveness. We will examine how government intervention can stimulate economic growth, redistribute income, enhance market efficiency, and address specific industry challenges.
By exploring real-world examples and empirical evidence, we aim to shed light on the intricate relationship between government intervention and economic outcomes.
Effects of Government Intervention
Government intervention in the economy refers to actions taken by the government to influence the allocation of resources, the level of economic activity, or the distribution of income. These interventions can take various forms, with varying degrees of impact on economic growth, income distribution, market efficiency, and specific industries.
Types of Government Intervention
- Fiscal policy:Involves government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand and economic growth.
- Monetary policy:Involves central bank actions to control the money supply and interest rates, influencing inflation, economic growth, and financial stability.
- Industrial policy:Involves government interventions in specific industries, such as subsidies, regulations, or direct ownership, to promote economic development or address market failures.
- Trade policy:Involves government actions to influence international trade, such as tariffs, quotas, or trade agreements, to protect domestic industries or promote economic growth.
- Social policy:Involves government programs and interventions aimed at addressing social issues, such as healthcare, education, or income inequality, to promote social welfare.
Effects of Government Intervention on Economic Growth, Micro topic 2.8 effects of government intervention
Government intervention can have both positive and negative effects on economic growth:
- Positive effects:Fiscal and monetary policy can stimulate aggregate demand, increase investment, and promote economic growth. Industrial policy can support innovation and foster the development of new industries.
- Negative effects:Excessive government spending and intervention can lead to inflation, debt accumulation, and reduced market efficiency. Industrial policy can lead to market distortions, inefficiency, and cronyism.
Effects of Government Intervention on Income Distribution
Government intervention can affect income distribution in several ways:
- Progressive taxation:Taxes levied on higher incomes at higher rates can reduce income inequality.
- Transfer payments:Government programs such as social security and unemployment benefits can provide a safety net for low-income individuals and reduce poverty.
- Education and healthcare subsidies:Government subsidies for education and healthcare can improve access to these essential services and reduce income inequality.
Effects of Government Intervention on Market Efficiency
Government intervention can have both positive and negative effects on market efficiency:
- Positive effects:Regulations can prevent market failures, such as monopolies or externalities, and promote fair competition.
- Negative effects:Excessive regulations can stifle innovation, reduce competition, and increase market distortions.
Government Intervention in Specific Industries
Government intervention in specific industries is often justified based on market failures or the need to achieve social goals:
- Healthcare:Government interventions aim to provide universal access to healthcare, control costs, and regulate the quality of care.
- Education:Government interventions aim to provide access to quality education, promote equity, and develop human capital.
- Energy:Government interventions aim to ensure energy security, promote renewable energy sources, and reduce environmental impact.
Q&A: Micro Topic 2.8 Effects Of Government Intervention
What are the main types of government intervention?
Government intervention can take various forms, including fiscal policy (e.g., taxation, spending), monetary policy (e.g., interest rate adjustments), regulation (e.g., environmental standards, antitrust laws), and industrial policy (e.g., subsidies, tariffs).
How does government intervention affect economic growth?
Government intervention can both stimulate and hinder economic growth. Well-designed interventions, such as infrastructure investment and education subsidies, can boost productivity and innovation. However, excessive intervention, such as чрезмерное регулирование, can stifle entrepreneurship and reduce economic efficiency.
What is the impact of government intervention on income distribution?
Government intervention can play a role in reducing income inequality through progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and minimum wage laws. However, it is important to consider the potential trade-offs, such as disincentives to work and reduced economic efficiency.
How does government intervention affect market efficiency?
Government intervention can both enhance and reduce market efficiency. Regulations aimed at correcting market failures, such as environmental protection and consumer protection laws, can improve market outcomes. However, excessive intervention, such as price controls and чрезмерное регулирование, can distort market signals and reduce economic efficiency.
What are some examples of government intervention in specific industries?
Examples of government intervention in specific industries include subsidies for renewable energy, regulations on healthcare providers, and tariffs on imported goods. These interventions aim to address specific market failures or policy objectives, such as promoting environmental sustainability, ensuring healthcare access, and protecting domestic industries.