Dive into the fascinating world of disease transmission with our comprehensive Disease Spread Gizmo Answer Key. Unravel the intricate mechanisms behind how diseases spread, empowering you with a deeper understanding of this critical topic.
Through interactive simulations, real-world examples, and expert insights, this guide provides an immersive exploration of the factors that influence disease spread, equipping you with the knowledge to effectively prevent and control the spread of infectious diseases.
Disease Transmission Methods: Disease Spread Gizmo Answer Key

Diseases can spread in various ways, each with unique characteristics and implications for prevention and control.
Direct Contact
Direct contact involves the transfer of pathogens from an infected individual to a susceptible individual through physical contact. Examples include:
- Skin-to-skin contact, such as touching or kissing
- Contact with bodily fluids, such as blood, saliva, or semen
- Contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
Indirect Contact
Indirect contact occurs when pathogens are transmitted through an intermediary object or substance. Examples include:
- Contact with contaminated food or water
- Inhalation of airborne droplets or aerosols containing pathogens
- Contact with contaminated soil or surfaces
Vectors, Disease spread gizmo answer key
Vectors are living organisms that transmit pathogens from one host to another. Examples include:
- Mosquitoes (malaria, dengue fever)
- Ticks (Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever)
- Fleas (plague, typhus)
Gizmo Simulations and Experiments

Gizmo simulations provide an interactive environment to explore the spread of disease and investigate factors that affect disease transmission. They can be used to conduct virtual experiments, manipulate variables, and observe the resulting changes in disease prevalence and transmission rates.
Gizmo Simulation: Disease Spread
The Disease Spread Gizmo simulates the spread of a contagious disease within a population. It allows users to adjust factors such as population size, transmission rate, recovery rate, and immunity level. By running the simulation multiple times with different settings, students can observe how these factors influence the spread of the disease.
Experiment: Effectiveness of Disease Prevention Measures
Using the Disease Spread Gizmo, students can design an experiment to test the effectiveness of different disease prevention measures, such as vaccination, quarantine, and social distancing. By comparing the results of simulations with and without these measures, students can evaluate the impact of each measure on disease transmission and identify the most effective strategies for preventing outbreaks.
Real-World Applications

Understanding the principles of disease spread is crucial for effective public health practices. By identifying transmission routes and risk factors, we can develop targeted interventions to prevent and control disease outbreaks.
Successful Disease Control Programs
Numerous disease control programs have successfully implemented strategies based on an understanding of disease transmission. Examples include:
- Polio vaccination:Widespread vaccination campaigns have led to the near-eradication of polio worldwide.
- Water sanitation:Improved access to clean water and sanitation systems has significantly reduced waterborne diseases like cholera and typhoid.
- Vector control:Mosquito control measures, such as spraying insecticides and draining breeding sites, have been effective in combating malaria and dengue fever.
Areas for Further Research
While we have made significant progress in understanding disease spread, further research is needed to:
- Emerging infectious diseases:Identify and monitor new disease threats and develop rapid response strategies.
- Antimicrobial resistance:Investigate the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance and develop new antibiotics to combat resistant bacteria.
- Environmental factors:Explore the role of environmental factors, such as climate change and urbanization, in disease transmission.
Data Analysis and Visualization

Analyzing and visualizing data is crucial for understanding disease transmission patterns and implementing effective control measures.
Through data analysis, we can identify high-risk populations, track disease spread, and evaluate the impact of interventions.
HTML Table
An HTML table is an effective way to organize data on disease transmission rates in different populations.
To unravel the intricacies of disease transmission, the disease spread gizmo answer key serves as an invaluable resource. Delving deeper into the realm of educational tools, the edmentum answer key english 1 provides a comprehensive guide to mastering the complexities of the English language.
Returning to the topic at hand, the disease spread gizmo answer key continues to illuminate the pathways through which infectious agents propagate.
- Rows represent different populations, while columns represent transmission rates for different diseases.
- This allows for easy comparison and identification of high-risk groups.
Graph
A graph can illustrate the relationship between population density and disease incidence.
- The x-axis represents population density, while the y-axis represents disease incidence.
- A positive correlation indicates that higher population density leads to higher disease incidence.
Map
A map can show the geographic distribution of a particular disease.
- Different colors or symbols represent different levels of disease prevalence.
- This helps identify areas with high disease burden and target interventions accordingly.
Educational Resources
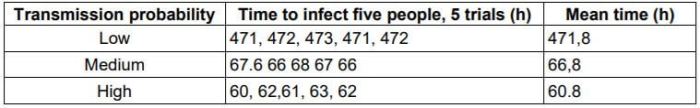
Understanding disease spread is crucial for preventing and controlling outbreaks. Numerous resources are available to provide information and facilitate teaching about this topic.
Online Resources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):The CDC provides comprehensive information on various diseases, including transmission methods, prevention, and control measures. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/how-covid-spreads.html
- World Health Organization (WHO):The WHO provides global health information, including disease outbreaks, prevention strategies, and resources for healthcare professionals. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus
- National Institute of Health (NIH):The NIH conducts research and provides information on various diseases, including their transmission, diagnosis, and treatment. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-funded-study-reveals-new-details-how-influenza-virus-spreads
Books and Articles
- Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice, Third Editionby Anne R. Pealer, MPH, PhD. This textbook provides a comprehensive overview of epidemiology, including disease transmission, outbreak investigation, and control measures.
- Emerging Infectious Diseases: A Guide for Clinicians and Public Health Professionalsby Pierre M. Buekens, MD, MPH, and Edward T. Ryan, MD. This book discusses emerging infectious diseases, their transmission, and strategies for prevention and control.
- The Germ Theory of Disease: A Historical Perspectiveby John M. Eyler. This book provides a historical account of the development of the germ theory of disease and its impact on our understanding of disease transmission.
Lesson Plan
Grade Level:High School Biology
Objectives:
- Students will understand the different methods of disease transmission.
- Students will be able to identify factors that influence disease spread.
- Students will be able to apply their knowledge to real-world examples of disease outbreaks.
Materials:
- Gizmo simulations: Disease Spread, Epidemic
- Real-world examples of disease outbreaks
- Whiteboard or chart paper
- Markers
Procedure:
- Begin by introducing the topic of disease spread and its importance in public health.
- Use the Gizmo simulation “Disease Spread” to demonstrate the different methods of disease transmission.
- Discuss the factors that influence disease spread, such as the mode of transmission, the population density, and the presence of vectors.
- Use the Gizmo simulation “Epidemic” to demonstrate how disease outbreaks can occur and spread.
- Present real-world examples of disease outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic or the Ebola outbreak in West Africa.
- Have students work in groups to develop a plan for preventing or controlling a disease outbreak.
- Conclude by summarizing the key points of the lesson and discussing the importance of understanding disease spread for public health.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary mode of disease transmission?
Direct contact with an infected individual or contaminated surfaces.
How can vectors contribute to disease spread?
Vectors, such as mosquitoes or ticks, can transmit diseases between hosts.
What is the significance of population density in disease transmission?
Higher population density increases the likelihood of contact between infected and susceptible individuals, facilitating disease spread.
