What is a enduring issue – What is an enduring issue? It’s a question that has puzzled scholars, policymakers, and everyday people for centuries. Enduring issues are those that persist over time, defying easy solutions and leaving a lasting impact on society. From poverty to climate change, these issues demand our attention and collective action.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the nature of enduring issues, examining their characteristics, consequences, and potential solutions. We’ll also explore historical and global perspectives, shedding light on the interconnectedness of these challenges and the urgency of addressing them.
Define Enduring Issue

An enduring issue is a topic or concern that has persisted over a long period of time and continues to be relevant and significant today. These issues are often complex and multifaceted, with multiple perspectives and no easy solutions.
Examples of enduring issues include:
- Climate change
- Poverty
- Racial inequality
- Gender discrimination
- Political polarization
Characteristics of Enduring Issues
Enduring issues are characterized by their longevity, complexity, and multifaceted nature. They persist over extended periods, transcending generations and societal changes. Their complex interconnections with various aspects of human existence make them challenging to resolve.
Factors Contributing to Persistence
Several factors contribute to the persistence of enduring issues:
- Deeply Rooted Causes:Enduring issues often stem from fundamental aspects of human society, culture, or the natural world. Addressing their root causes requires comprehensive and sustained efforts.
- Competing Interests:Different stakeholders often hold opposing views and priorities regarding enduring issues, making it difficult to reach consensus and implement solutions.
- Limited Resources:Resolving enduring issues requires significant resources, both financial and human. Resource constraints can hinder progress and prolong their persistence.
li> Lack of Political Will:Political leaders may prioritize short-term gains over long-term solutions to enduring issues, leading to a lack of sustained commitment and action.
Impact of Enduring Issues

Enduring issues have profound and far-reaching consequences that reverberate throughout society, economy, and politics. Their impact is multifaceted and often disproportionately affects certain groups, exacerbating social and economic inequalities.
The social consequences of enduring issues are undeniable. They can erode trust in institutions, undermine social cohesion, and foster feelings of alienation and disenfranchisement. For example, persistent poverty and inequality can lead to social unrest and violence, while discrimination and racism create barriers to opportunity and perpetuate cycles of disadvantage.
Economic Impact
Enduring issues also have a significant economic impact. They can hinder economic growth, reduce productivity, and exacerbate poverty. For instance, climate change poses a major threat to economic stability, as it can disrupt supply chains, damage infrastructure, and lead to loss of livelihoods.
Similarly, armed conflict and political instability can disrupt trade, investment, and tourism, resulting in economic decline.
Political Impact, What is a enduring issue
The political consequences of enduring issues can be equally profound. They can undermine democratic institutions, erode public trust, and polarize society. For example, persistent political corruption can weaken the rule of law and lead to a loss of faith in government.
Similarly, unresolved ethnic or religious conflicts can create political instability and hinder peace and reconciliation.
Disproportionate Impact
It is important to recognize that enduring issues often have a disproportionate impact on certain groups within society. Marginalized and vulnerable communities, such as low-income families, racial minorities, and indigenous populations, are often disproportionately affected by these issues. They may face greater barriers to accessing education, healthcare, and employment, and are more likely to experience poverty, discrimination, and social exclusion.
Addressing Enduring Issues

Addressing enduring issues is crucial for the progress and well-being of societies. Various approaches have been employed to tackle these complex and persistent problems.
One approach involves the implementation of policies and regulations that aim to address the root causes of enduring issues. These policies may include measures to reduce poverty, promote education, or protect the environment. By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to these issues, policies can strive to create a more equitable and sustainable society.
International Cooperation
Enduring issues often transcend national boundaries and require global cooperation to effectively address them. International organizations such as the United Nations play a vital role in facilitating collaboration between nations, coordinating efforts, and providing resources to tackle these challenges.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities is essential for addressing enduring issues. By involving affected individuals and groups in the decision-making process, their perspectives and experiences can be incorporated into solutions. Community engagement empowers individuals and fosters a sense of ownership, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation and sustainable outcomes.
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in addressing enduring issues. By educating the public about the nature, causes, and consequences of these problems, individuals can become more informed and motivated to take action. Raising awareness can also help to reduce stigma and discrimination associated with certain enduring issues, creating a more inclusive and supportive society.
Case Studies
Enduring issues are complex problems that persist over time and affect various aspects of society. To better understand these issues, let’s examine specific case studies that highlight their causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Climate Change
Climate change is an enduring issue with far-reaching implications. It is primarily caused by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Consequences of climate change include rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in plant and animal life. It poses significant risks to human health, ecosystems, and the global economy.
Addressing climate change requires a multi-faceted approach. Mitigation efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and sustainable land use practices.
Adaptation measures aim to prepare for the unavoidable impacts of climate change, such as building sea walls to protect coastal communities and developing drought-resistant crops.
Examples of Enduring Issues
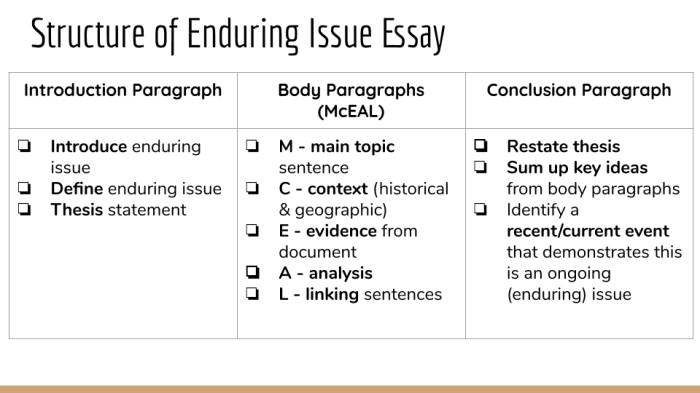
Enduring issues are complex problems that have persisted over time and continue to impact societies worldwide. They defy easy solutions and require sustained attention and collaborative efforts to address their root causes and mitigate their consequences.
The following table provides examples of enduring issues, their underlying causes, potential consequences, and possible solutions:
Table of Enduring Issues
| Issue | Cause | Consequence | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poverty | Economic inequality, lack of access to education and employment opportunities, political instability | Social unrest, health problems, environmental degradation | Investment in education and job creation, social welfare programs, equitable distribution of resources |
| Climate Change | Greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, industrialization | Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity | Transition to renewable energy, sustainable land use practices, carbon capture and storage technologies |
| Conflict and War | Political, economic, and social grievances, competition for resources | Human suffering, displacement, economic disruption | Diplomacy, peace negotiations, conflict resolution mechanisms, economic development |
| Health Disparities | Inequitable access to healthcare, poverty, environmental factors | Poor health outcomes, reduced life expectancy, social inequality | Universal healthcare, improved access to nutritious food and clean water, public health initiatives |
Historical Perspective: What Is A Enduring Issue
Enduring issues have a long and complex history, spanning centuries and even millennia. These issues have evolved over time, influenced by social, political, economic, and technological changes.
In the early days of human civilization, enduring issues such as conflict, inequality, and resource scarcity were primarily addressed through traditional customs, religious beliefs, and tribal laws. As societies became more complex, formal systems of government and law were developed to address these issues on a larger scale.
Evolution of Enduring Issues
The evolution of enduring issues can be traced through major historical events and periods. For example, the Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in the way that goods were produced and consumed, leading to new challenges related to labor rights, environmental pollution, and economic inequality.
Similarly, the rise of globalization in the late 20th century has had a profound impact on enduring issues such as cultural identity, economic interdependence, and global conflict. The increasing interconnectedness of the world has both created new opportunities and exacerbated existing challenges.
Throughout history, enduring issues have continued to shape the course of human events. They have been the driving force behind wars, revolutions, and social movements. Understanding the historical context of these issues is essential for developing effective strategies to address them in the present and future.
Global Context
Enduring issues transcend national borders and impact multiple regions around the world. They are interconnected, often exacerbating or mitigating one another, creating a complex web of challenges.
Globalization and advancements in technology have further intertwined the world, making enduring issues even more interconnected. For example, climate change affects all regions, regardless of their level of development or political systems. Similarly, economic inequality can have ripple effects across borders, as financial crises in one region can impact economies worldwide.
Global Cooperation
Addressing enduring issues from a global perspective requires international cooperation and collaboration. Multilateral organizations, such as the United Nations, play a crucial role in facilitating dialogue, coordinating efforts, and setting global agendas. By working together, nations can pool their resources, share knowledge, and develop innovative solutions to common challenges.
Regional Alliances
In addition to global cooperation, regional alliances can also play a significant role in addressing enduring issues. Regional organizations, such as the European Union or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), can foster cooperation among neighboring countries, promote economic integration, and address shared challenges.
An enduring issue refers to a persistent problem or challenge that remains unresolved over time. In the context of legal disputes, enduring issues can involve complex legal questions that require careful consideration and interpretation. One such case is Dalal v.
City of New York , which raises important questions regarding the rights of individuals in the face of government actions. Enduring issues often require ongoing attention and effort to find equitable and lasting solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, enduring issues are multifaceted challenges that have persisted throughout history and continue to impact societies worldwide. Understanding the nature and consequences of these issues is crucial for informed decision-making and sustainable solutions.
Addressing enduring issues requires a collaborative effort involving individuals, communities, and governments. By fostering critical thinking, promoting dialogue, and implementing evidence-based policies, we can work towards mitigating the impact of these challenges and creating a more just and equitable world.
FAQ
What is the key characteristic of an enduring issue?
Enduring issues are characterized by their persistence over time, defying easy solutions and leaving a lasting impact on society.
What are some examples of enduring issues?
Poverty, climate change, racial inequality, and political polarization are just a few examples of enduring issues that have persisted for decades or even centuries.
Why is it important to address enduring issues?
Enduring issues have a profound impact on our societies, affecting economic growth, social stability, and environmental sustainability. Addressing these issues is essential for building a more just, equitable, and sustainable world.